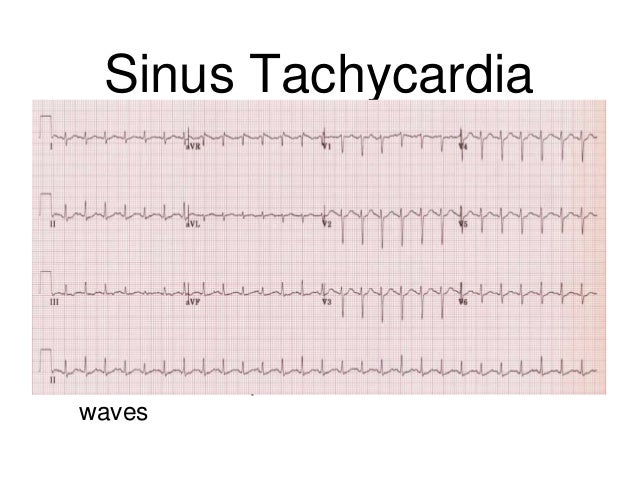
√無料でダウンロード! sinus tachycardia ecg tracing 182428-Sinus tachycardia ecg tracing
PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an atrial infarction) Ventricular Aneurysm The ECG patternHome » ECG » Sinus node dysfunction Find a tracing Library / Pathology s Sinus node dysfunction Sinoatrial arrest Library Conduction disorders Pathology Sinus node dysfunction sinusIe, it starts and ends abruptly
Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia With Adenosine
Sinus tachycardia ecg tracing
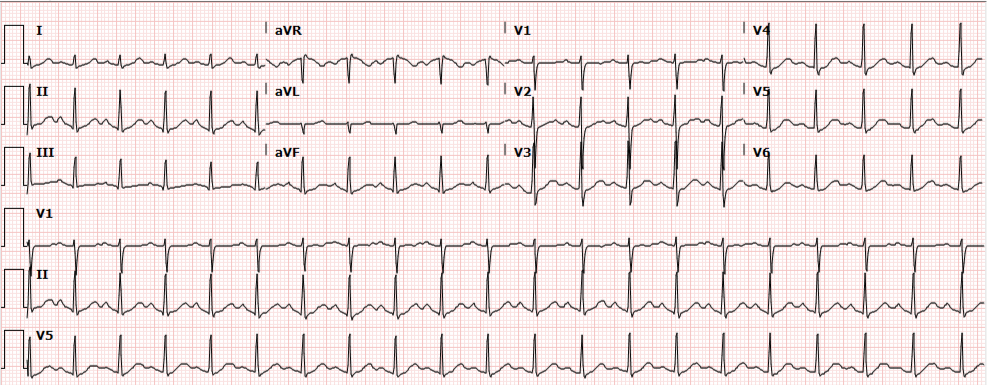
Sinus tachycardia ecg tracing-Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 21 ratio Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias ;As having sinus tachycardia and 1° AV block Clinical Scenario The ECG in the Figure was obtained from a 61yearold woman who was being treated with flecainide for "arrhythmia" Her tracing was interpreted as showing sinus tachycardia with 1° AV block, with the conduction disturbance being seen best in lead V 1



Tachycardia Acls Wiki
· This electrocardiogram (ECG) shows rapid monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT), 280 beats/min, associated with hemodynamic collapse The tracing was obtained from a patient with severe ischemicThe heart arrhythmia practice drills provide a test EKG tracing and users are asked to identify the type of arrhythmia Many of these drills include tachycardia EKG tracings Each answer is immediately evaluated and the correct classification of the EKG tracing is provided, along with a detailed explanationAn EKG, also called an ECG or electrocardiogram, is a recording of the heart's electrical activity It is a quick and painless procedure EKGs captures a tracing of cardiac electrical impulse as it moves from the atrium to the ventricles These electrical impulses cause
Lowvoltage QRS complexes microvoltages;Atrial fibrillation definitions, causes, risk factors, ECG diagnosis and management Atrial fibrillation is the most common pathologic tachyarrhythmia (only sinus tachycardia is more common) Prevalence of atrial fibrillation correlates strongly with age Approximately 10% of individuals aged 80 years and above have atrial fibrillationThe patient was very dehydrated The physicians were worried about STEMI, and so did a Point of Care Cardiac Ultrasound which showed IVC collapse and
Abstract We present the case of a young male patient in sinus rhythm whose electrocardiogram (ECG) was initially misinterpreted as ventricular tachycardia Electrocardiographic artifact appearing to be ventricular tachycardia commonly occurs and ECG criteria have been described to aid in the discrimination between artifact and true arrhythmia There are many causes of artifactsThe ECG criteria for sinus tachycardia including causes and treatment are discussed in this review The syndrome of inappropriate sinus tachycardia SIST is mentioned Sinus Tachycardia ECG · There are two formulas to determine the rate of an ECG tracing Rate = 1500 / No of small boxes between R – R interval;



Focal Atrial Tachycardia Fat Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Ecglibrary Com Normal Adult 12 Lead Ecg
In this video we take a look at the basic components of sinus tachycardia Be sure to visit our website, EMTprepcom for more great trainingThis video is spBelhassen et al observed that this tachycardia can be terminated by the calcium channel blocker verapamil3 This observation has been confirmed subsequently by others as well4,5,6,7 Belhassen et al proposed that this is a specific ECGelectrophysiological entity8 Fascicular tachycardia has also been called Idiopathic Left Ventricular Tachycardia (ILVT) by other authors, though left · The rhythm in ECG #1 is not sinus tachycardia We know this is — because although there is atrial activity, the P wave in lead II is negative (slanted RED arrows) Unless there is lead misplacement or dextrocardia — a negative P wave in lead II excludes the possibility of a sinus




Sinus Tachycardia Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
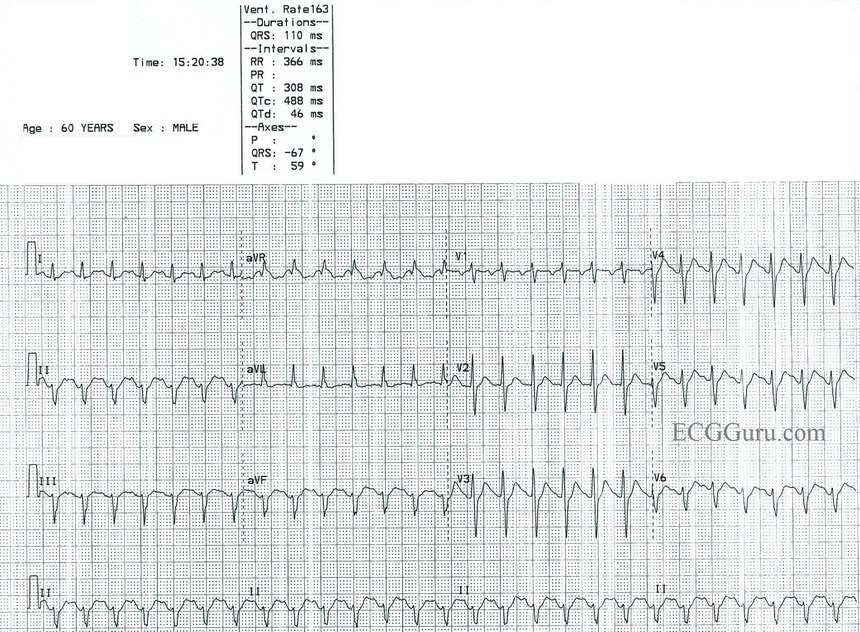



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference
· The ECG in today's case shows a supraventricular rhythm at a rate just over 100/minute The QRS complex appears to be slightly wide, albeit with a supraventricularlike morphology most consistent with marked LVHand possible incomplete LBBB The cardiac rhythm is uncertain The rhythm could be sinus tachycardia with 1stdegree AV block — orFinally the T wave may be an upward or downward deflection of the ECG tracing;EKG Tracing Please refer to the EKG tracing below if you are not familiar with the labeling of the EKG waveforms Figure 1 EKG Tracing Step 1 Rate The first step is to determine the RATE, which can be eyeballed by the following technique Locate the QRS (the big spike) complex that is closest to a dark vertical line Then count either forward or




Sinus Bradycardia Wikipedia




Irregular Narrow Complex Tachycardia Circulation
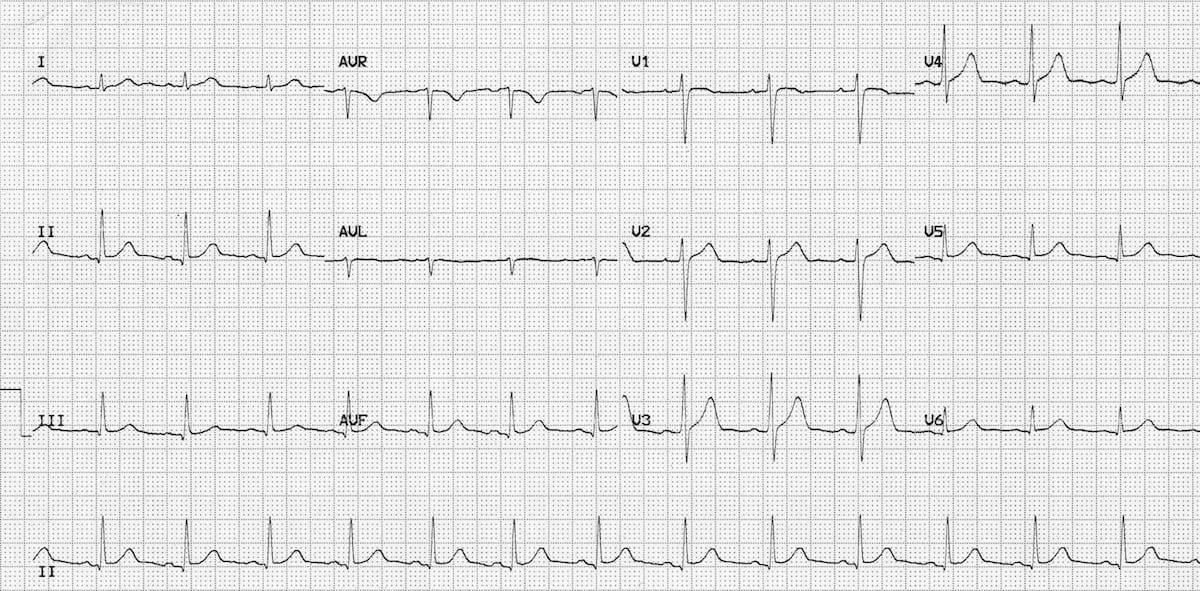
· An ECG was obtained for tachycardia First ECG Sinus tachycardia at 150 There is inferior ST Elevation and Qwaves that appear to be Inferior STEMI There is reciprocal ST depression in aVL Is this STEMI?Sinus Node Reentrant Tachycardia (SNRT) Caused by reentry circuit close to or within the sinus node;May terminate with vagal manoeuvres;
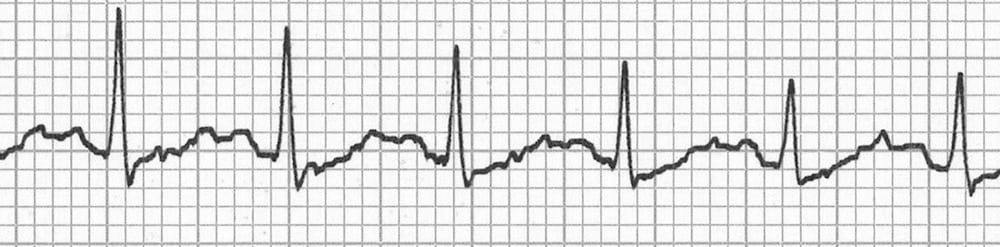



Sinus Tachycardia Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
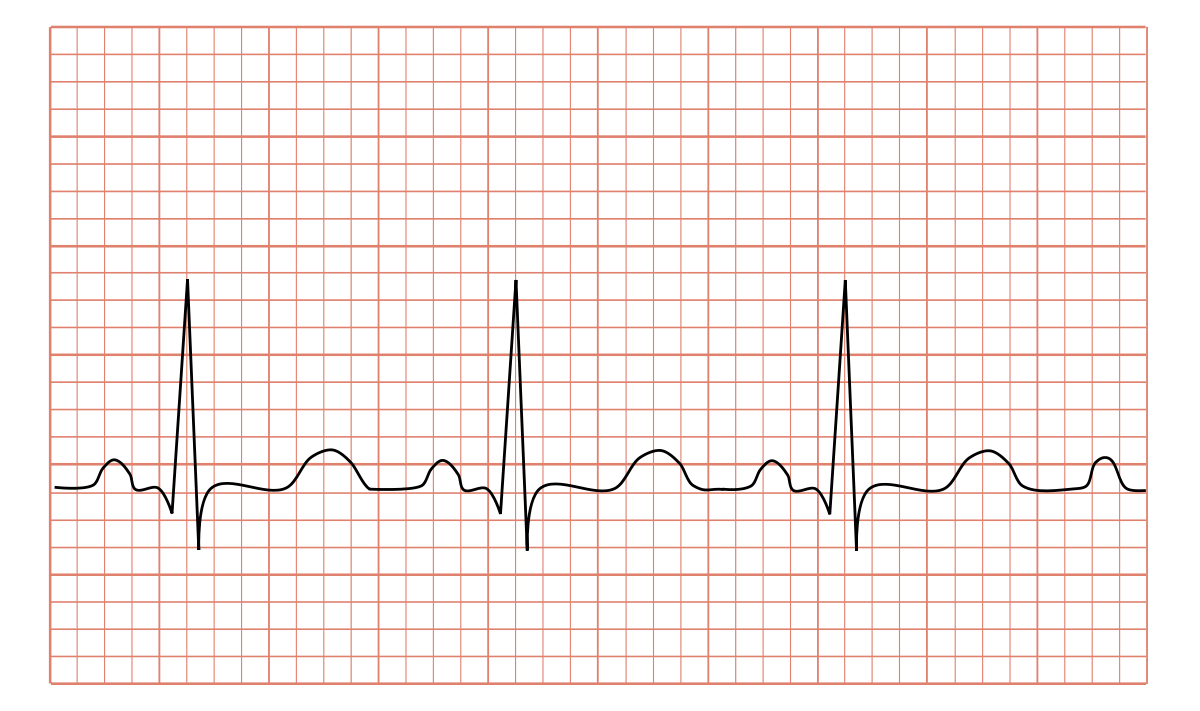



Tachycardia Wikipedia
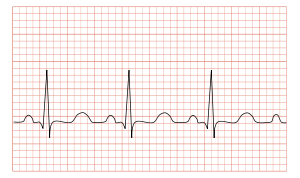
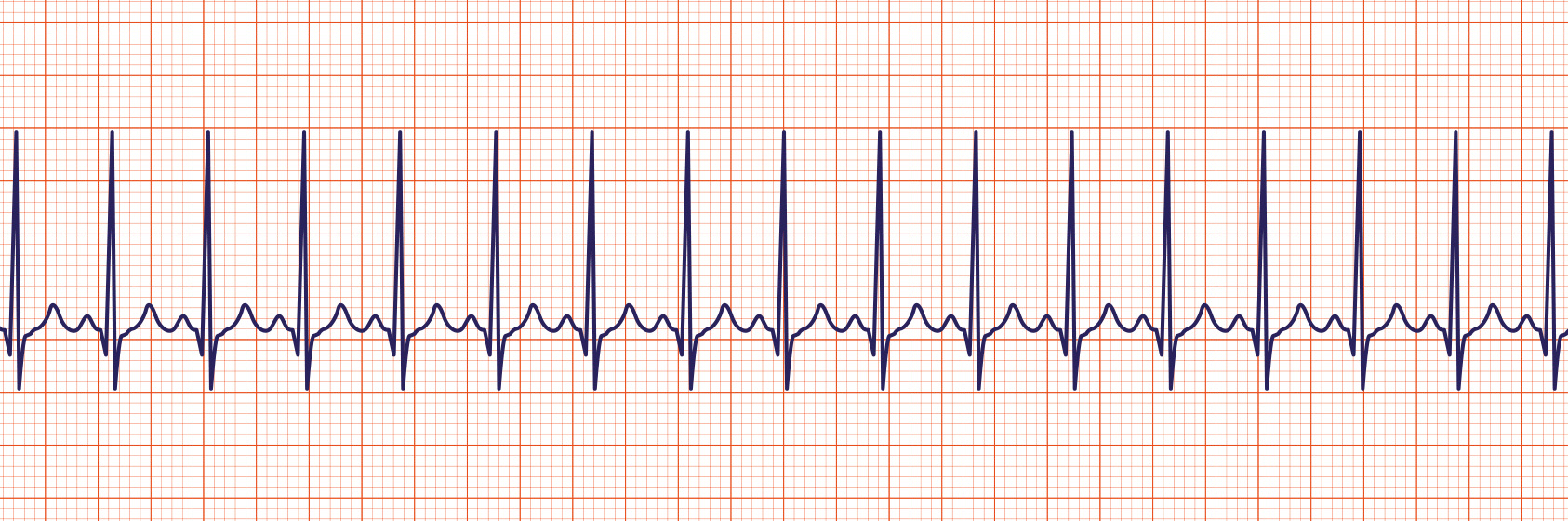
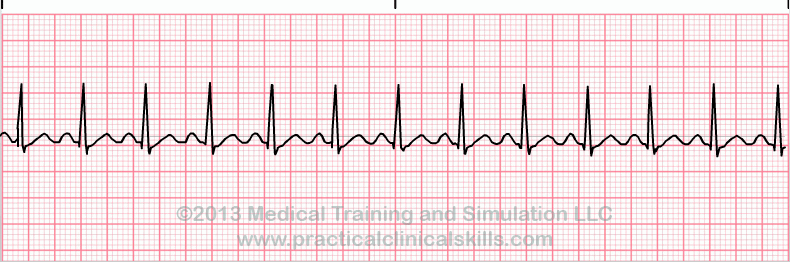
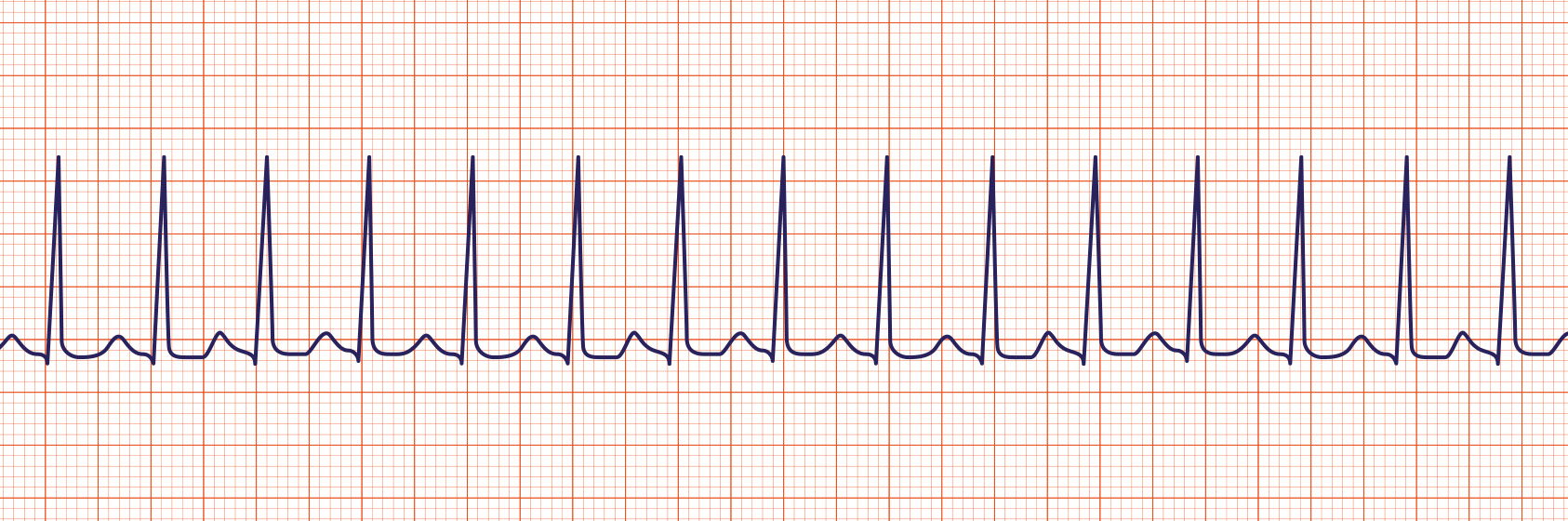
Rate usually 100 – 150 bpm;Disorder in which the sinoatrial · Sinus tachycardia refers to an increased heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute (bpm) The sinus node, or sinoatrial node, is a bundle of
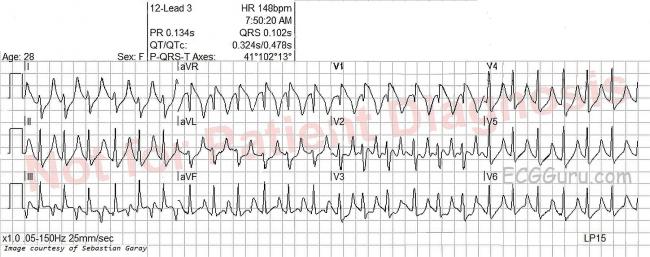



Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
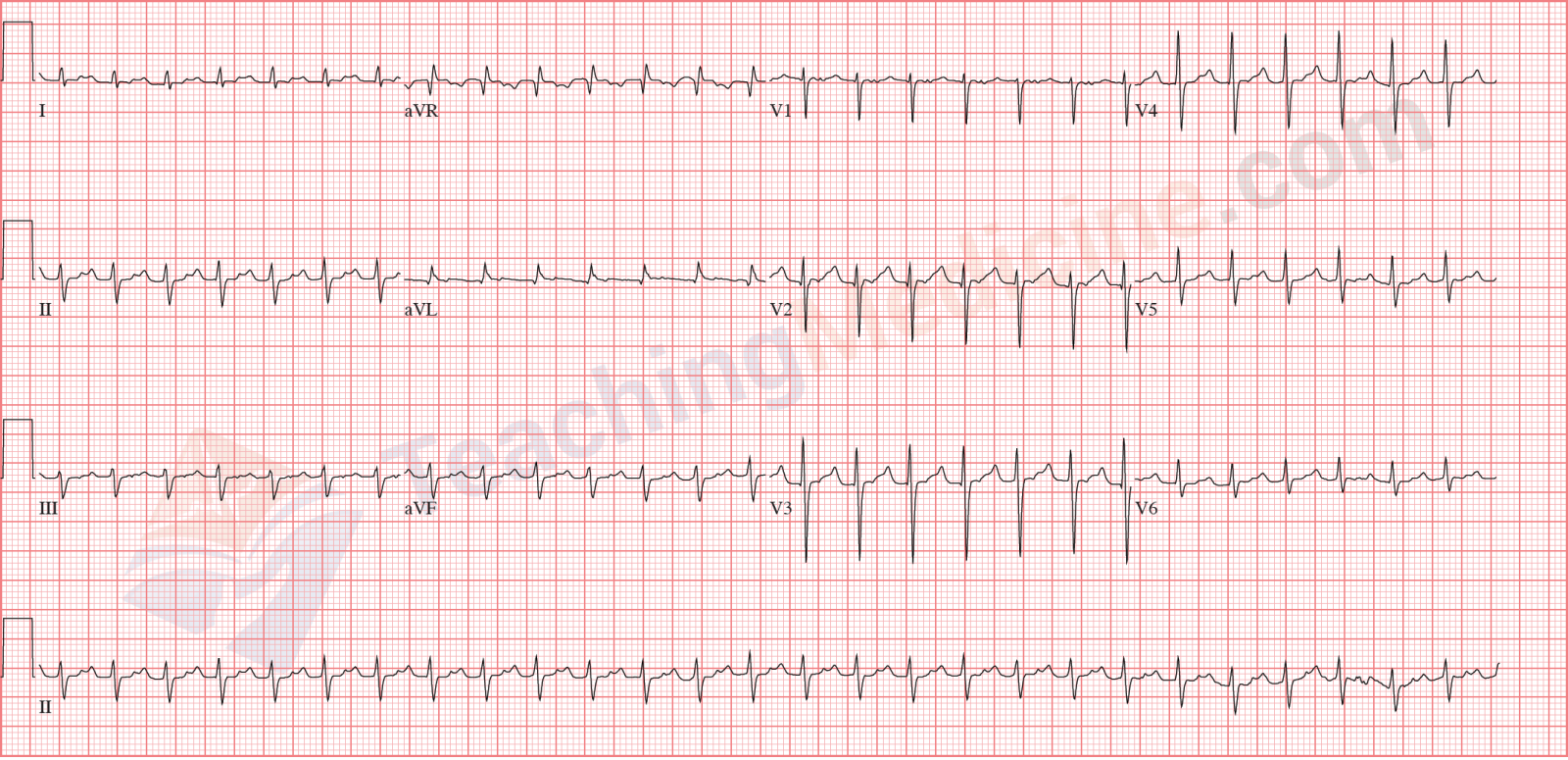
ECG tracing discrete regular P waves often different from the sinus P waves Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts Atrial tachycardia bursts of atrial tachycardia (10 beats in the middle section of the rhythm strip II at bottom) follows sinus complexes From the collection of Dr Arti N Shah Citation endsSinus bradycardia occurs on an ECG when there is a normal upright P wave in lead II ― sinus P wave ― preceding every QRS complex with a ventricular rate of less than 60 beats per minute99 · In contrast to the left precordial leads (V2–6), the precordial V1 lead showed sinus tachycardia;



Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia Arrhythmia Alliance



Tachycardia Wikipedia
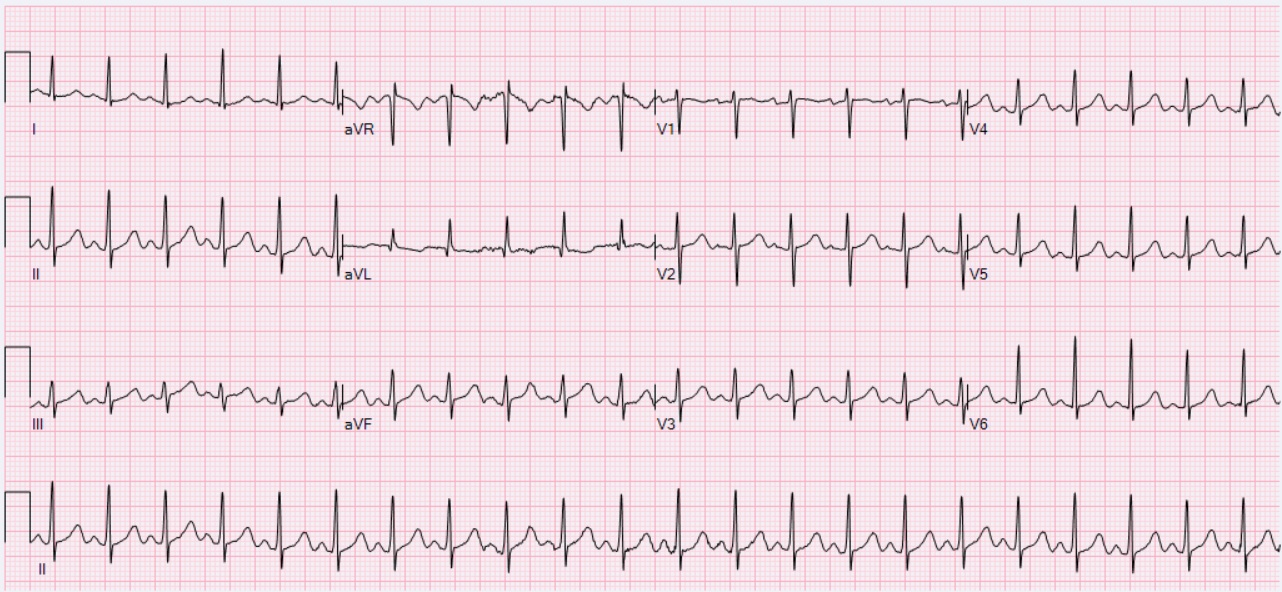
· Sinus tachycardia refers to a fasterthanusual heart rhythm Your heart has a natural pacemaker called the sinus node, which generates electricalQRS complexes found in a 6second portion of the ECG tracing • The 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 method involves locating an R wave on a bold line on the ECG paper, then finding the next consecutive R wave and using the 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 values for subsequent bold lines to determine the rate • To use the 1500 method count the number of small squares between twoThe 3channel ECG tracing above is from a 24hour ECG (rhythm Holter) recording The third P wave from the left side has a different morphology (an atrial premature contractionAPC) The second APC starts a shortlasting atrial tachycardia episode The last two beats are sinus beats




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Chest Pain Sinus Tachycardia And St Elevation




Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Ekg Grepmed
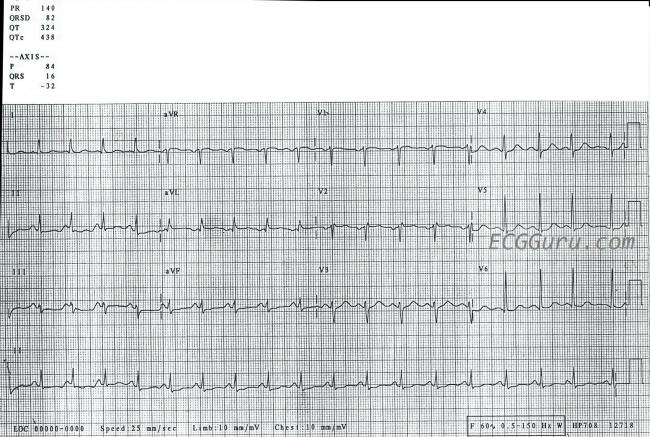
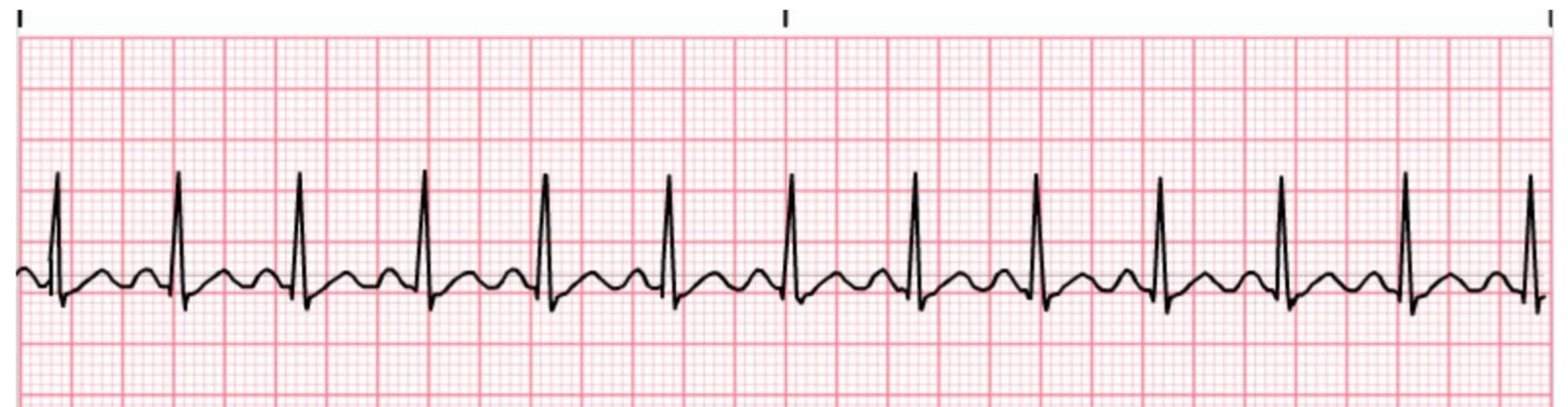
· This ECG is from a collection of tracings that, sadly, have no patient information It is interesting nonetheless, and we would love to hear your thoughts on it ECG Findings The rhythm is sinus tachycardia, at a rate of 1 bpm The QRS is narrow at 08 seconds ( ms) While the PR interval is normal, at 14 seconds (140 ms), the PR segment · The ECG shows Sinus tachycardia; · ECG indistinguishable from sinus tachycardia;



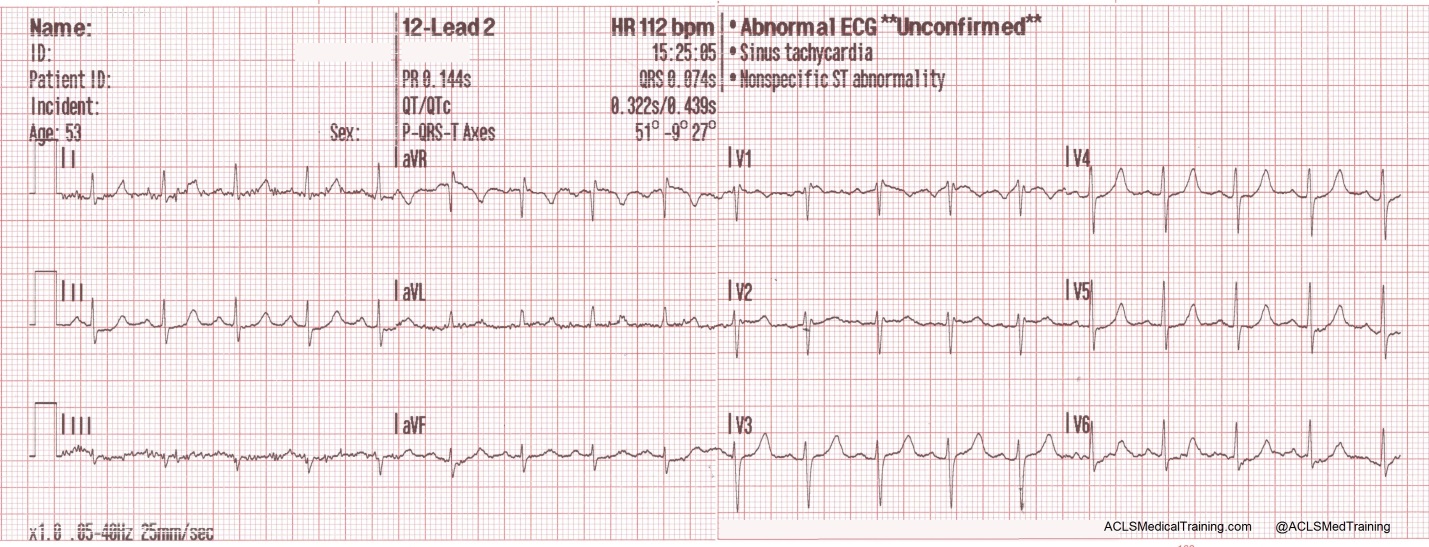
Rhythm Recognition Acls Medical Training




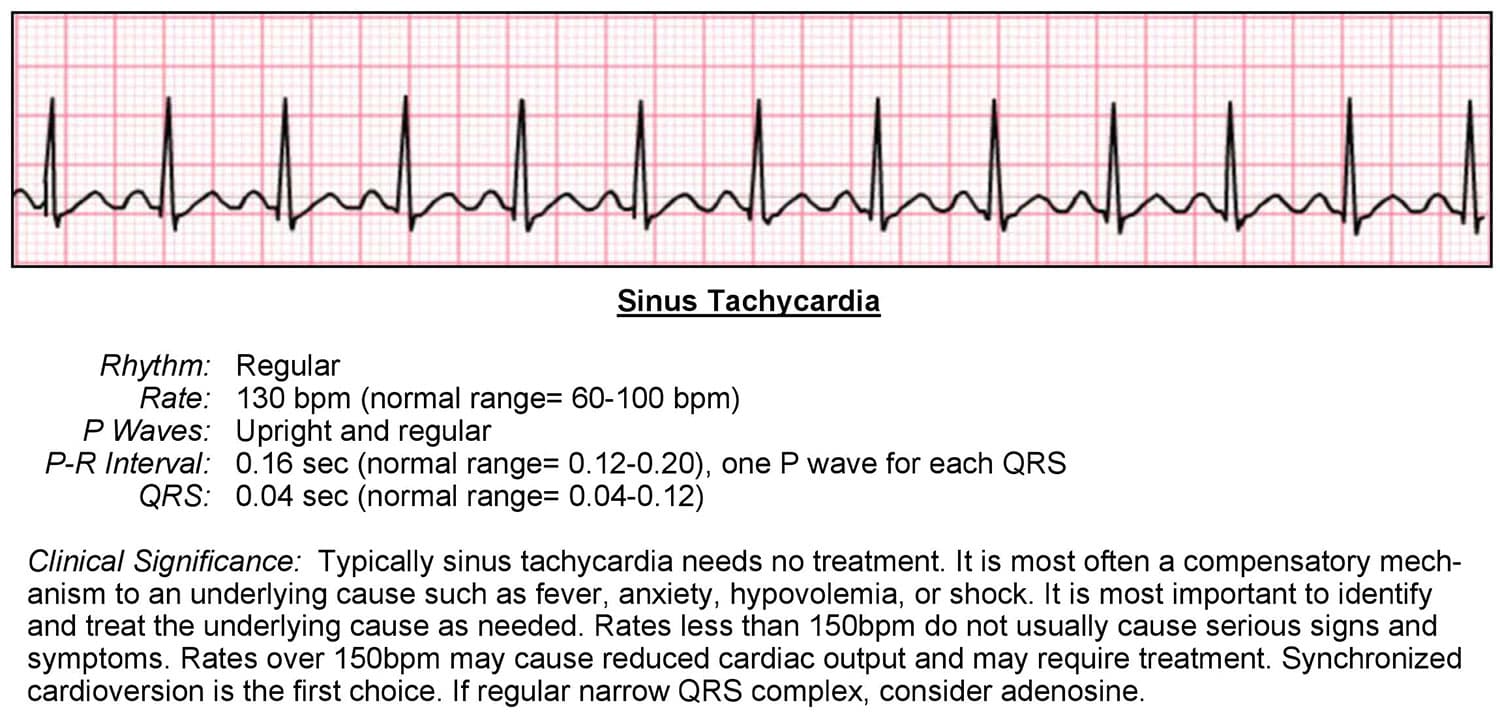
Tachycardia Acls Wiki
The shape of the electrocardiogram (EKG) tracing will exhibit certain key attributes to be considered normal, as discussed below With normal sinus rhythms, the heart beat's electrical impulse originates in the sinoatrial node (SA) The P waves are upright and appear before each QRS and have the same shapeSinoAtrial Reentrant Tachycardia This is a rare form of PSVT where the reentrant circuit is between the sinus node and the right atria The ECG looks like sinus tachycardia, but the tachycardia is paroxysmal;The WPW ECG, seen in the diagram, shows a short PR, delta wave, and somewhat widened QRS SinoAtrial Reentrant Tachycardia This is a rare form of PSVT where the reentrant circuit is between the sinus node and the right atria The ECG looks like sinus tachycardia, but the tachycardia is paroxysmal;




Ecg Quiz Very Wide And Very Fast Emergency Physicians Monthly



Cardiology Pance And Panre Content Blueprint High Yield Combined Review Smarty Pance
Tachycardia (tachyarrhythmia) with narrow QRS complexes (QRS durationSinus tachycardia is sinus rhythm with a rate of > 100bpm Sinus tachycardia is an example of a supraventricular rhythm In sinus tachycardia the sinus node fires between 100 and 180 beats per minute, faster than normal The maximal heart rate decreases with age from around 0 bpm toSinus Tachycardia with PVCs for an ECG machine This video is provided by Cascade Healthcare Services, A leading provider of healthcare training courses incl



Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




12 Lead Ekg Interpretation Understanding 12 Lead Ekg
Sinus tachycardia, antiPMT algorithm and proarrhythmogenic effect Tracing N° 5 Manufacturer Boston Scientific Device CRT Field Effort Patient A 51year old male patient with a history of ischemic cardiomyopathy with left bundle branch block was implanted with a triplechamber Boston Scientific Incepta CRTD Interrogation revealed PMTExplanation To determine the actual rhythm on an ECG tracing, the ECG technician gathers data about the characteristics of the tracing and then matches the information to the specific ECG rhythm criteria to classify the various cardiac dysrhythmias Although some ECG machines provide an interpretation, only the physician can view this interpretation and determine whether it is · Sinus tachycardia is usually a secondary condition Inappropriate sinus tachycardia is a primary condition diagnosed in patients with symptomatic persisting sinus tachycardia in which the below causes have been excluded




Pediatric Ekg Interpretation



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
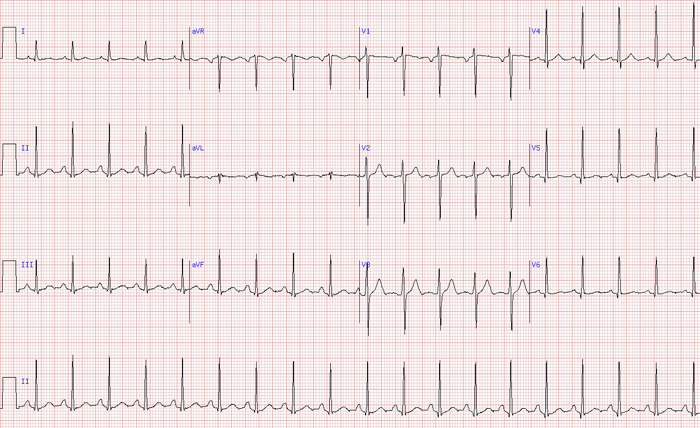
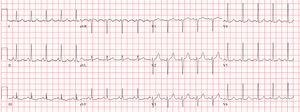
· Non–LifeThreatening Condition (IV) Artifact Simulating a Run of Ventricular Tachycardia At first glance, this ECG suggests a run of ventricular tachycardia However, sharp deflections occur regularly at the same rate as the sinus rhythm seen at the beginning and at the end of the tracing ( black doubleheaded arrows )B Posttachycardia sinus pause in a patient with TachyBrady Syndrome c Artifact the ECG lead fell off the patient d Vagal reaction with dramatic sinus pause e Complete AV block with premature atrial contractionIn sinus rhythm when the SA node is the pacemaker, the mean direction of atrial depolarization These machines make a 12lead ECG tracing over a 10second period One row starts with lead I, switches to aVR to be followed by V1, and ends with V4 A second row starts with lead II and records aVL, V2, and V5 in sequence while a third row records lead III, aVF, V3, and V6 in



Sinus Tachycardia Ecgpedia




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Alcohol Withdrawal And Sinus Tachycardia
ECG Examples Example 1a SlowFast (Typical) AVNRT Narrow complex tachycardia at ~ 150The T wave is a measure of ventricular recovery prior to the next contraction • Irregular heartbeats (known as "arrhythmias") noted with sick sinus syndrome include any or all of the following inappropriate slow heart rate (known as "sinus bradycardia");Abrupt onset and termination;




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn



1
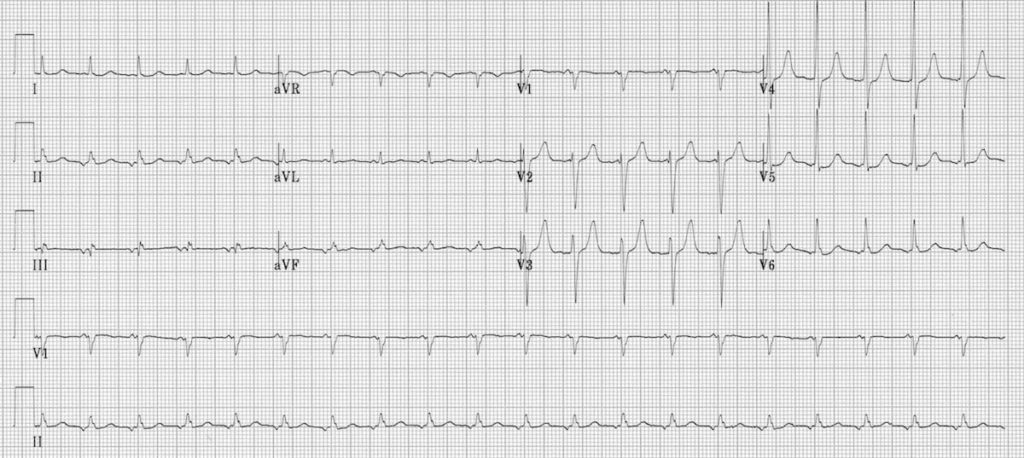
Rate = 300 / No of larges boxes between R – R interval < 60 bpm – Bradycardia < 100 bpm – Tachycardia Cardiac Axis Average direction of spread of the depolarization wave through the ventricles as seen from the front is called the cardiac axis FirstSinus tachycardia is the most common tachyarrhythmia (tachycardia) Sinus tachycardia is the result of an increased rate of depolarization (ie increased automaticity) in the sinoatrial node This simply means that the sinoatrial node discharges electricalTherefore an ECG in the dextrocardia position was taken by positioning the precordial leads rightwards on the chest This right sided ECG showed ventricular tachycardia in V1R whereas precordial leads V2R–6R showed sinus rhythm (fig 1)




Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia Ektopik Atriyal Tasikardi Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com




Electrocardiogram Showing Sinus Tachycardia At 1 Beats Min With Low Download Scientific Diagram
Sinus tachycardia is the most common perioperative rhythm abnormality and is almost always benign It is characterized by a heart rate between 100 and 160 beats/minute The ECG demonstrates a regular rhythm with a normal P wave before each QRS complex · ECG Findings The rhythm is sinus tachycardia, at a rate of 1 bpm The QRS is narrow at08 seconds ( ms) While the PR interval is normal, at14 seconds (140 ms), the PR segment is very short The PR segment is the line between the end of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complexClose Enable Notifications OK No thanks OK No thanks



Focal Atrial Tachycardia Fat Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



File Ecg Sinus Tachycardia 132 Bpm Jpg Wikimedia Commons
ECG 1 In the ECG above, atrial tachycardia with 31 block is seen Only 1 of every 3 P waves is conducted to the ventricles The atrial rate is about 0/minute and isoelectric baseline can be observed between P waves Dr Peter Kukla has donated this ECG to our websiteIe, it starts and ends abruptly 8 Junctional Rhythms and Tachycardias · RHYTHM ECG rhythm characterized by a usual rate of anywhere between 6099 bpm, every P wave must be followed by a QRS and every QRS is preceded by P wave Normal duration of PR interval is 35 small squares The P wave is upright in leads I and II Normal Sinus Rhythm 36 Sinus Bradycardia RHYTHM Rate < 60bpm, otherwise normal 37




Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosis And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor



Rhythm Recognition Acls Medical Training
P wave morphology is normal;ECG MONITORING The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic tracing of the electrical impulses produced in the heart ECG waveforms are produced by the movement of charged ions across the semipermeable membranes of myocardial cells There are 12 recording leads in the standard ECG




Sinus Tachycardia Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Mcgill Ekg Learning Project



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead



Ecg Analysis



Teaching Medicine Tutorial Rhythm Diagnostic Criteria



No Doubling The Paper Speed Will Not Reveal Hidden P Waves Ems 12 Lead



February Ecg Lesson Emergency Medicine Guidewire
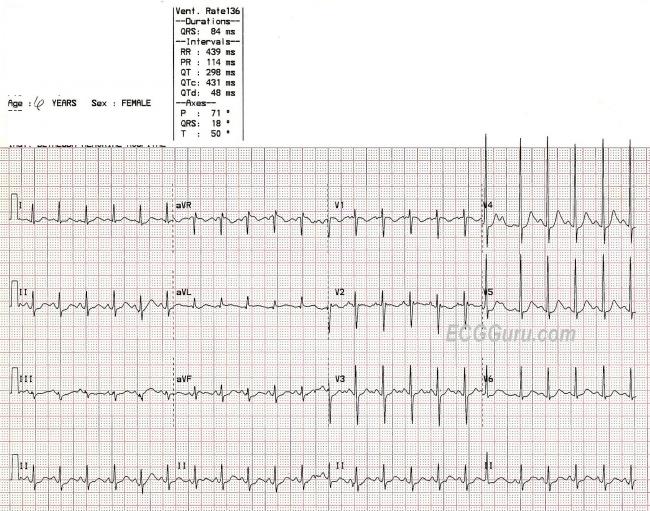



Sinus Tachycardia In A Child Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ecg On Admission Sinus Tachycardia At 103 Bpm No Evidence Of Ischemic Download Scientific Diagram



Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Background Etiology Epidemiology



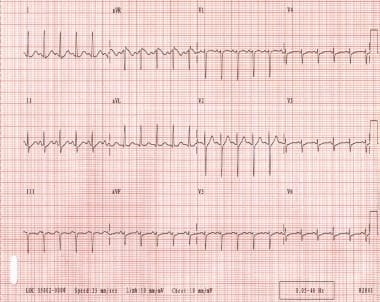
Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources




Ecg Shows Sinus Tachycardia With Widespread St Elevation Pr Elevation Download Scientific Diagram




Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia Ektopik Atriyal Tasikardi Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com




Electrocardiogram Sinus Tachycardia Download Scientific Diagram



Figure 1 Ekg Of The Patient At Presentation Demonstrates Sinus Tachycardia Right Ventricular Hypertrophy With Repolarization Abnormality Aorta Right Atrial Tunnel Causing Heart Failure In A Young Female Science And Education Publishing
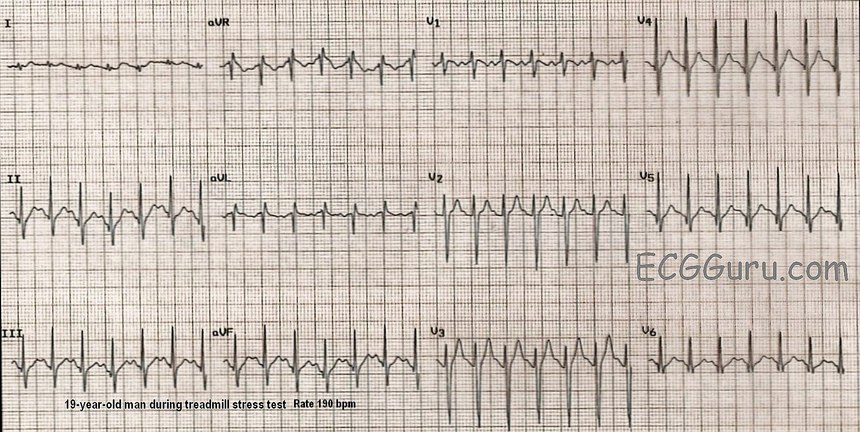



Sinus Tach Or Svt 4 Clues To Tell The Difference




Atrial Tachycardia Diagnosis And Treatment The Cardiology Advisor




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Ekg At The Time Of Admission Shows Sinus Tachycardia And Inferior Download Scientific Diagram




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Chest Pain Sinus Tachycardia And St Elevation
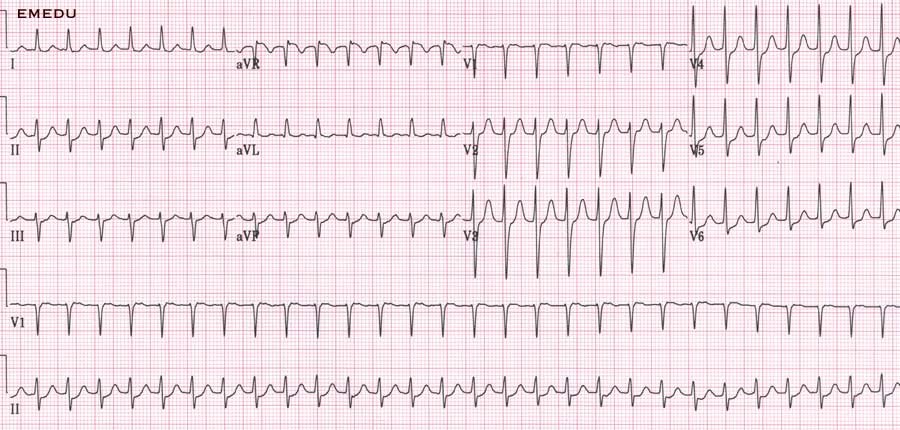



Ecg Ekg Examples And Quiz Oxford Medical Education




Ecg Educator Blog Sinus Tachycardia




The Electrocardiogram Showed Sinus Tachycardia St Elevation And Q Wave Download Scientific Diagram




Pin On Public Health Medicine Nursing Dentistry Case Management Research International Medicine



Mcgill Ekg Learning Project



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Artifact Versus Arrhythmia In Pseudo Polymorphic Tachycardia Case Rep Rrcc



File 12 Lead Sinus Tachycardia Young Jpg Wikimedia Commons




Pin On Hemo




Dr Smith S Ecg Blog Tachycardia Dehydration And New St Elevation In A Something Then A Surprise
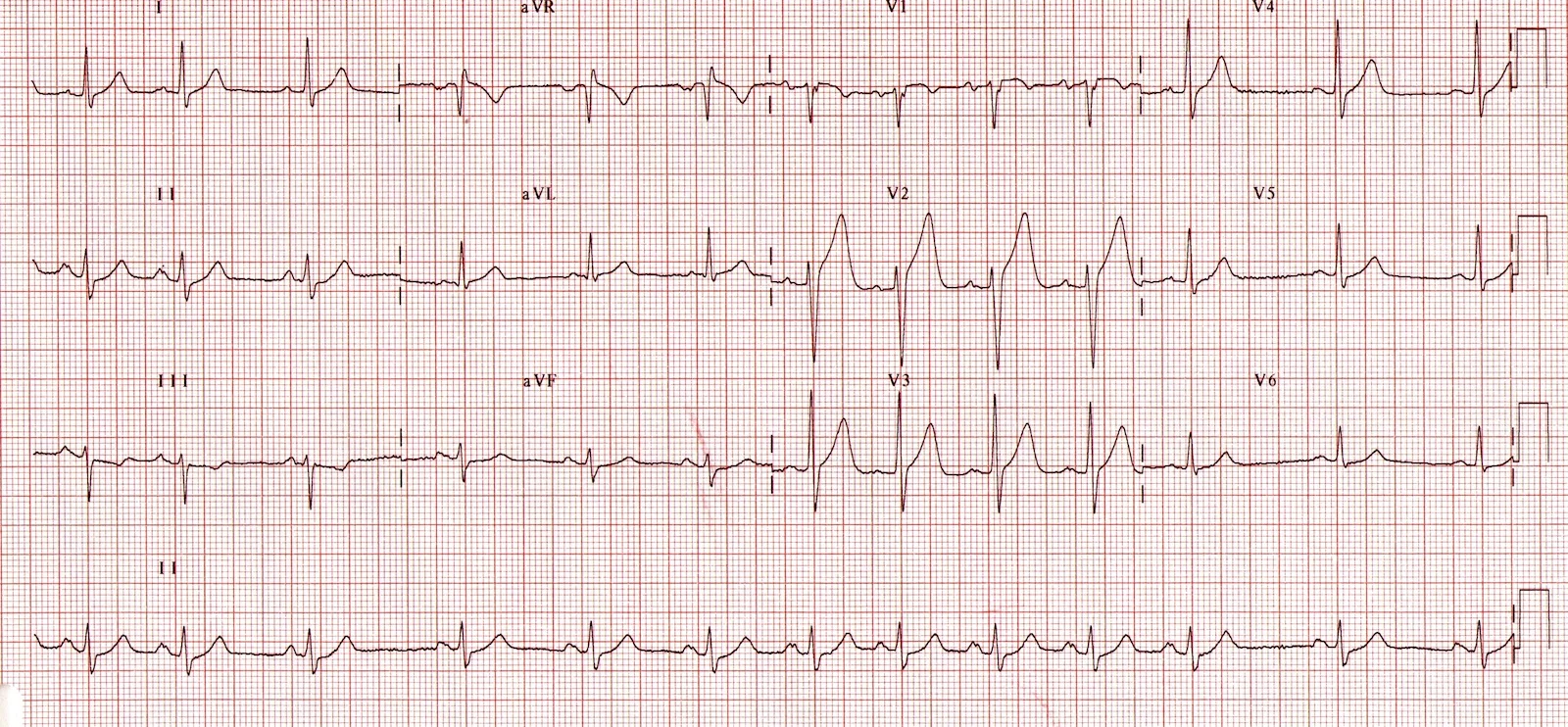



Ecgs Ekgs The Simtech



Snell Pym Sinus Tachycardia
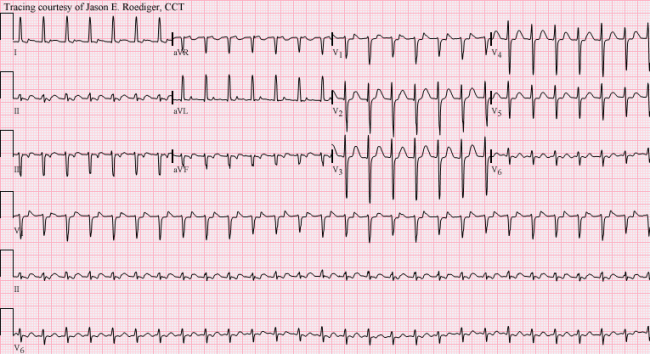



Sinus Tachycardia Page 2 Ecg Guru Instructor Resources
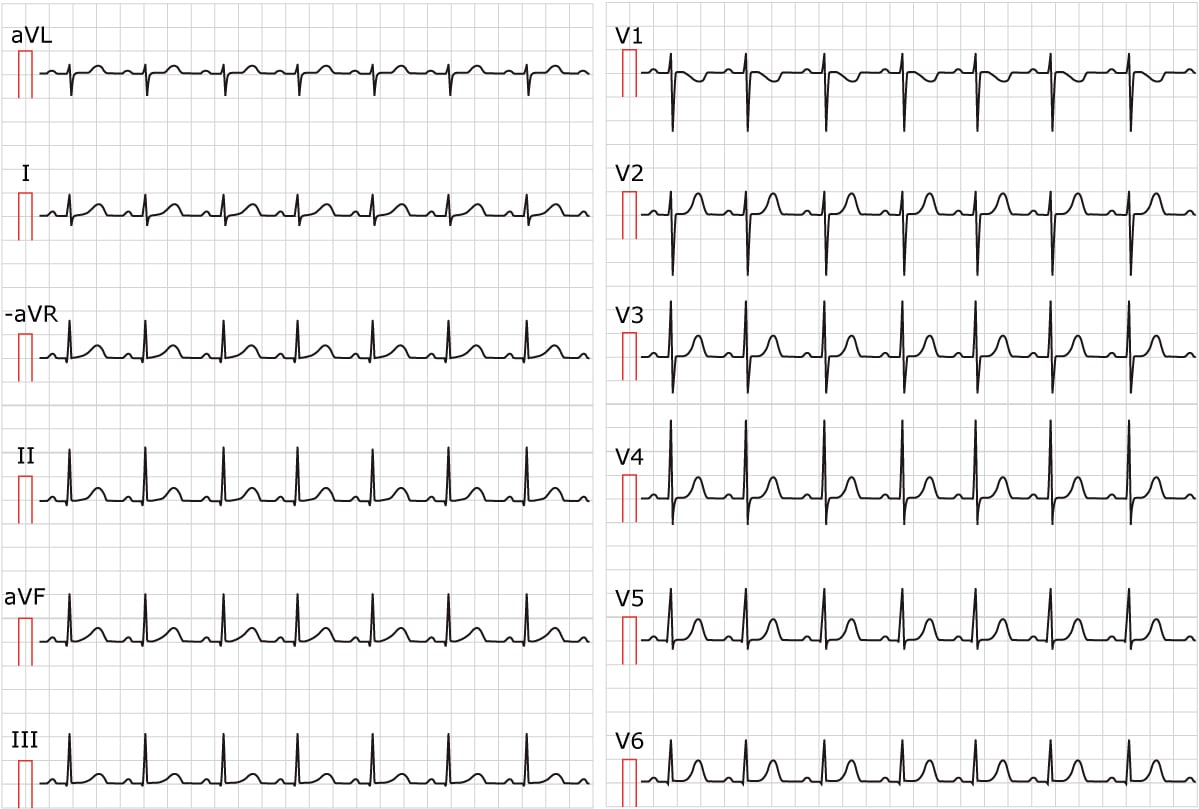



Sinus Tachycardia Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Echo



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
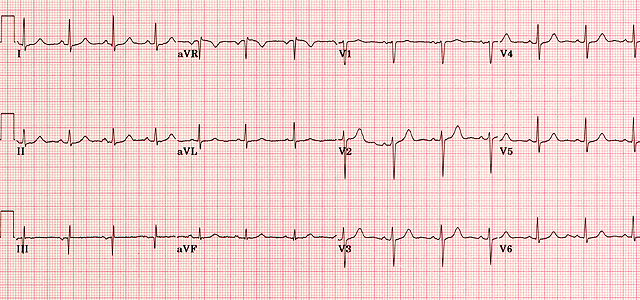



Normal Ecg




How To Identify Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Stripe Sinus Tachycardia Ecg Findings Ecg Questions Youtube




Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 72 Sinus Tachycardia In A Child Juvenile T Wave Variant Baseline Wander Artifact




Sinus Tachycardia Wikipedia




Sinus Rhythms Medictests



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead



10 Tips To Diagnose Atrial Flutter On An Ekg



The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead




Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia With Adenosine



Q Tbn And9gcsiiuwyirizwffk67aig3fx Hqe40soqstmyg 8qmx5ymq5lado Usqp Cau




Sinus Tachycardia Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com



Ecg Changes In Pulmonary Embolism New Health Advisor



Differential Diagnosis Of Sinus Tachycardia




Ecg Sinus Tachycardia Youtube




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography




Sinus Tachycardia Ekg L The Ekg Guy Ekg Md Cute766



Normal Sinus Rhythm Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Em Cases Ecg Cases 19 Tachycardias




Sinus Arrhythmia Ecg High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Ekg Showing Sinus Tachycardia With 1 1 Conduction On Day 6 Download Scientific Diagram




Ecg Interpretation Of Arrhythmias Tusom Pharmwiki



Q Tbn And9gcrj7jjxc7qhufopyxh0dmynfaarb1a8793s5qx8ro7 Budmdsrb Usqp Cau



Sinus Tachycardia Training Cardiac Arrhythmias Video Propals




Sinus Tachycardia Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




File Ecg Sinus Tachycardia 125 Bpm Jpg Wikipedia
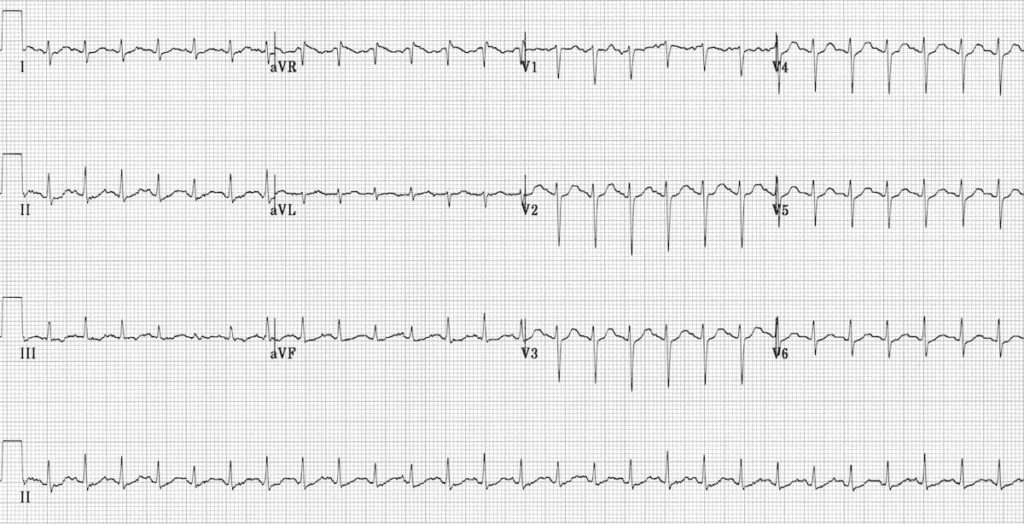



Sinus Tachycardia Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Ekg Demonstrating Sinus Tachycardia With A Rate Of 125 Normal Axis Download Scientific Diagram



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



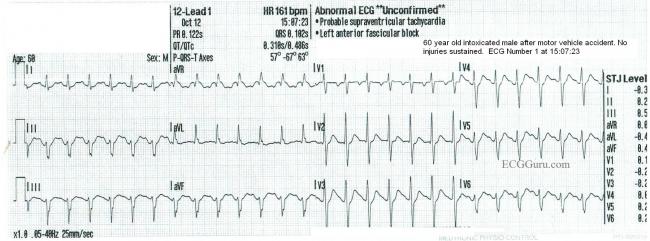
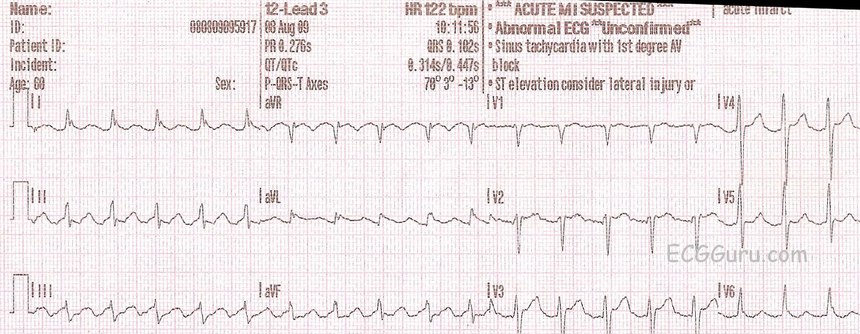
Solved 12 Lead Ekg Name Id 12 Lead3 Hr 105 Bom Borderline Ecg Unconfirmed Patient Id Sinus Tachycardia Pr 8 1509 Ors 8 2s Rightward Course Hero
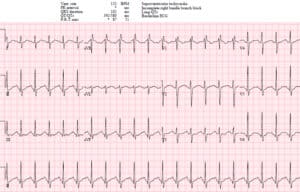



Em Cases Ecg Cases 19 Tachycardias




Irregular Narrow Complex Tachycardia Circulation



1



The Trouble With Sinus Tachycardia Ems 12 Lead
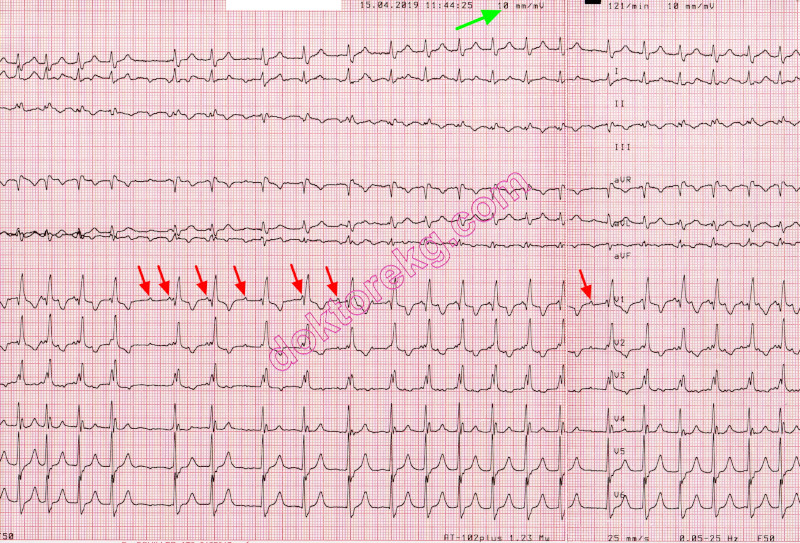



Sinus Tachycardia Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
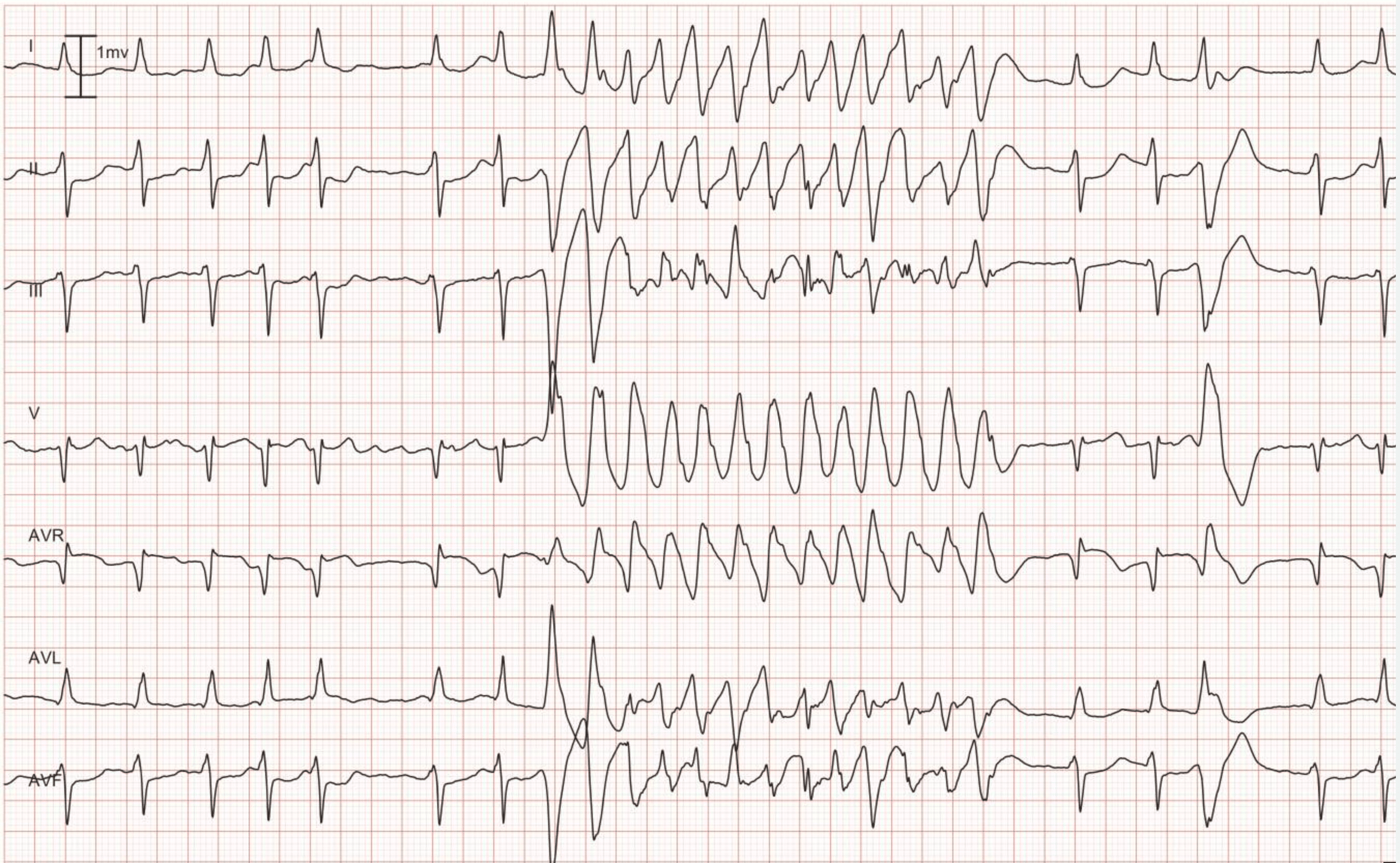



Ventricular Tachycardia Vt Ecg Criteria Causes Classification Treatment Management Ecg Echo



Supraventricular Tachycardia Vs Sinus Tachycardia Epomedicine


コメント
コメントを投稿